Like our Earth, The Moon is also composed of a core, mantle, and crust. At the center, there is a solid inner metallic core mainly composed of iron and a small amount of Nickel. Covering the inner core there is a molten outer core which increases the length of the core to 330 km.
Above the core are the mantle and crust. Differences in compositions between these layers tell a story of the Moon being largely, or even completely, composed of a great ocean of magma in its very early history.
As the magma ocean began to cool, crystals began to form within the magma. Crystals of denser mantle minerals, such as olivine and pyroxene sank down to the bottom of the ocean.
Lighter minerals, notably anorthositic plagioclase feldspar, crystalized and floated to the surface to form the Moon’s crust.
The crust has a thickness of about 43 miles (70 kilometers) on the Moon’s near-side hemisphere and 93 miles (150 kilometers) on the far-side. It is made of oxygen, silicon, magnesium, iron, calcium and aluminum, with small amounts of titanium, uranium, thorium, potassium and hydrogen.
Long ago the Moon had active volcanoes, but today they are all dormant and have not erupted for millions of years.
Surface
With a very thin atmosphere and a weak magnetic field, a steady rain of asteroids, meteoroids and comets strikes the surface of the Moon, leaving numerous craters behind. Tycho Crater is more than 52 miles (85 kilometers) wide.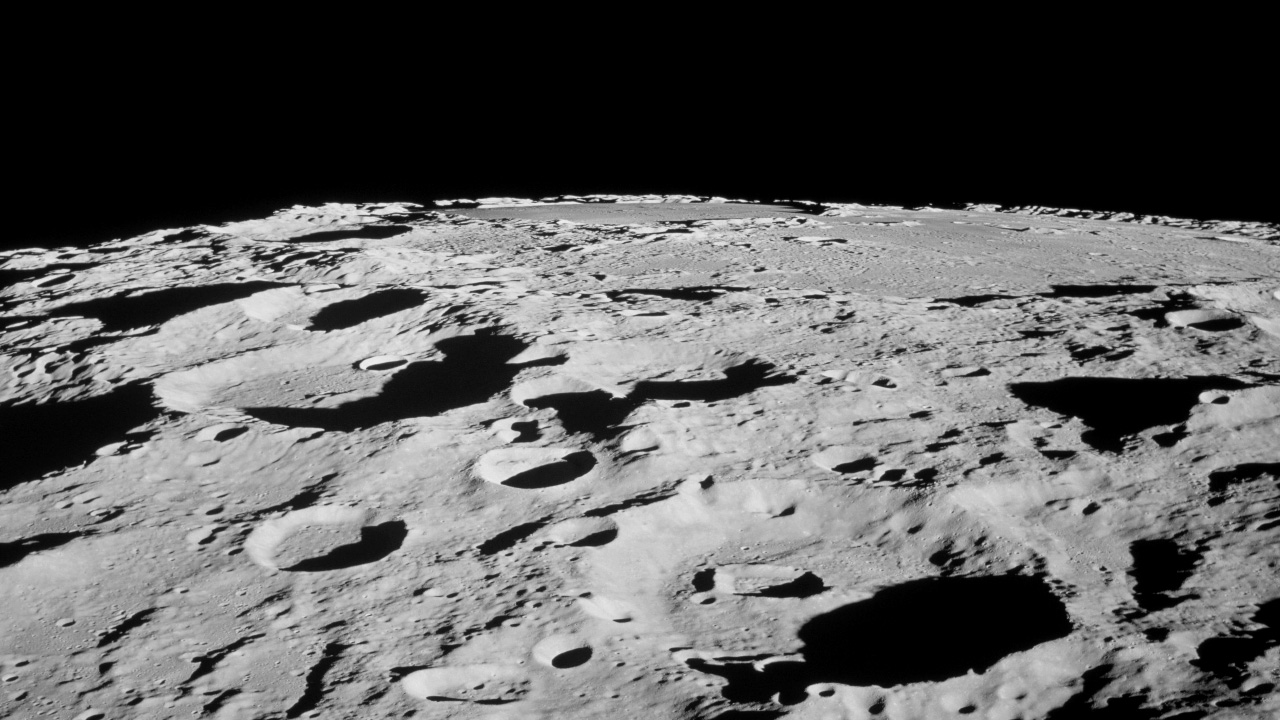
Over billions of years, these impacts have ground up the surface of the Moon into fragments ranging from huge boulders to powder. Nearly the entire Moon is covered by a rubble pile of charcoal-gray, powdery dust and rocky debris called the lunar regolith. Beneath is a region of fractured bedrock referred to as the megaregolith.
The temperature reaches about 260 degrees Fahrenheit (127 degrees Celsius) when in full sun, but in darkness, the temperature falls down to about -280 degrees Fahrenheit (-173 degrees Celsius).
Water on the Moon
During the initial exploration of the moon, and the analysis of all the returned samples from the Apollo and the Luna missions, we thought that the surface of the moon was dry.
The first definitive discovery of water was made in 2008 by the Indian mission Chandrayaan-1, which detected hydroxyl molecules spread across the lunar surface and concentrated at the poles. Missions such as Lunar Prospector, LCROSS, and Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, have not only shown that the surface of the Moon has global hydration, but there are actually high concentrations of ice water in the permanently shadowed areas of the lunar surface.
Atmosphere and Magnetic Field
The Moon has a very thin and weak atmosphere, called an exosphere. It does not provide any protection from the sun's radiation or impacts from meteoroids.
The early Moon may have developed an internal dynamo, the mechanism for generating global magnetic fields for terrestrial planets, but today, the Moon has a very weak magnetic field. The magnetic field here on Earth is many thousands of times stronger than the Moon's magnetic field.
Potential for Life
The many missions that have explored the Moon have found no evidence to suggest it has its own living things. However, the Moon could be the site of future colonization by humans. The discovery of the Moon harbors water ice, and that the highest concentrations occur within darkened craters at the poles, makes the Moon a little more hospitable for future human colonists.
In the coming years, Nasa is looking forward to send its astronauts back to the surface of the moon by 2024. The advantage that we will get after making a human base on the moon is that we will require less fuel to pursue our missions to other planets like Mars and moons like Titan. And also it will be a big achievement for mankind towards space development.
Importance Of Moon
Our natural satellite moon which is one-fourth of the size of the earth but has a major contribution in making life possible on earth.
In its early stages, the earth rotates very fast and at that time, one day was only of 8 hours but after the formation of the moon, the earth experiences a gravitational force by the moon due to which its rotational speed has slowed down, increasing the length of the day to 24 Hours.
Another importance of Moon is that it makes the earth to be tilted at 22 and a half degrees which cause seasons on the Earth.
It also causes tides, creating a rhythm that has guided humans for thousands of years.
Thanks for giving your time to this post. Have a nice day.






Comments
Post a Comment